This is my guide to search engine optimization (SEO) basics for all you beginners out there.
If you want to:
- Learn why SEO is important and how it works.
- Discover the different types of SEO and their benefits.
- Get some actionable tips on how to use SEO for your website.
Then this is the blog you’ve been waiting for.
Let’s jump right into it.
What Is SEO?
SEO is the art and science of optimizing your website to rank highly in search engine results.
It helps you to understand the intricate workings of search engines and implement certain strategies.
By doing this, you’ll drive organic traffic, gain visibility, and connect with your target audience.
Unlike paid advertising strategies, the results generated by SEO appear as organic search results. These results are based on the quality and relevance of the web pages that match the search intent for the given search query.
A Very Brief History of SEO
To some of us, it might feel like SEO has been around FOREVER. Of course, this isn’t the case.
It’s thought that the term was created in 1997.
The early days of SEO were a simpler time when search engines used fairly basic algorithms to rank content. In turn, this meant that SEO was relatively simple too.
Now, Google and other search engines use advanced algorithms to filter out low-quality content and prioritize relevance.
So, SEO has had to continuously evolve to keep up.
Why SEO Is Important
If you have a website, you want to attract as much traffic to that site as possible, right?
Well, when it comes to search engines most people click on the first few search results towards the top of the SERP. Research has shown that ranking in the top spot of the SERP results in a CTR (click-through rate) of 39.8%. This drops to 18.7% for the second position and 10.2% for the third position. As you can see, this is a HUGE difference.
Therefore, SEO is important because it helps your webpages to rank high up on the SERPs. This means your page could be one of the first results people see when they search for things related to the content on your site.
When your website ranks highly, it leads to increased traffic and increased leads.
But how do Google and other search engines work?
Since Google is by far the most used search engine in the world, let’s focus on that.
First, Google analyzes the structure of your website through crawling.
Crawling is the process where search engine crawlers (also known as bots) systematically explore and analyze webpages by following links. Google then indexes the content on your site.
OK, but now you’re probably wondering what on earth indexing is.
Indexing is the process Google uses to store and organize the information its bots have collected from crawling your web pages. This information is stored in a huge database called the Google index.
Then, Google uses complex algorithms to determine the rankings of your pages in the SERP. The rankings are based on many different factors including the relevance of your content, the backlinks you have acquired from other sites, and the authority of your site.
But here’s the catch—Google’s ranking criteria are constantly evolving.
This means it’s really important that you stay up-to-date with Google’s latest guidelines and recommendations. If you do, you’ll have a better chance of keeping your rankings nice and high.
How Does SEO Work?
Search engine optimization includes different elements such as On-page and Off-page SEO, Technical SEO, and Local SEO. They’re all important parts of SEO that ultimately help your site to gain more traffic and better rankings.
On-page SEO uses techniques such as creating quality content, using relevant keywords and optimizing the headings of your content.
Off-page SEO takes place outside of your website and involves things like building backlinks and social media marketing.
Technical SEO looks at optimizing the speed of your website, using XML sitemaps, ensuring mobile-friendliness, amongst other things.
Don’t worry, I’ll cover all of this in greater detail soon.
They’re all important parts of SEO that work together to ultimately help your site to gain more traffic and better rankings.
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO means optimizing the elements that are on your web pages rather than off-page elements like backlinks.
Keyword Research and Analysis
Identifying Your Keywords
OK, first, you need to figure out what you actually want to rank for. This will be based on the products or services you offer. Or, on the type of content you provide on your site.
To do this, you need to identify the terms and phrases people search for when looking for content related to your business. In SEO, these terms are known as keywords.
As an example, let’s say you run a plumbing business. You could optimize your webpages for keywords like ‘plumbing services’, ‘residential plumbing services’, or ‘commercial plumbing services ‘. Plus, you can target keywords that are specific to your location. This could be ‘plumbing services in Phoenix’, for example.
However, when you do your keyword research there are several factors you need to take into account.
Search Volume
The first factor is search volume. This shows you how many people are searching for a specific keyword. If lots of people are searching for a keyword, that’s great. Just bear in mind that this often also means it’ll be harder to rank for that keyword.
You can find a keyword’s search volume using Semrush’s Keyword Overview tool. To use it, you simply type your keyword into the search bar, click ‘search’, and Semrush will provide you with an overview of the search volume.
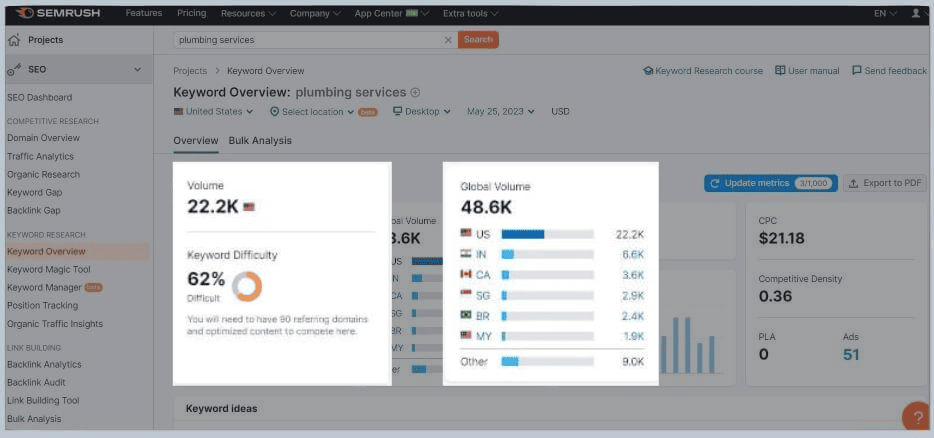
Keyword Difficulty
Keyword research also involves assessing the competition for specific keywords. This means determining what the relative competition is for a keyword and how likely you are to rank for it. When you’re just starting out, you want to target terms with low keyword difficulty so that you can start improving your rankings quickly. These will often be long-tail keywords (more on that later).
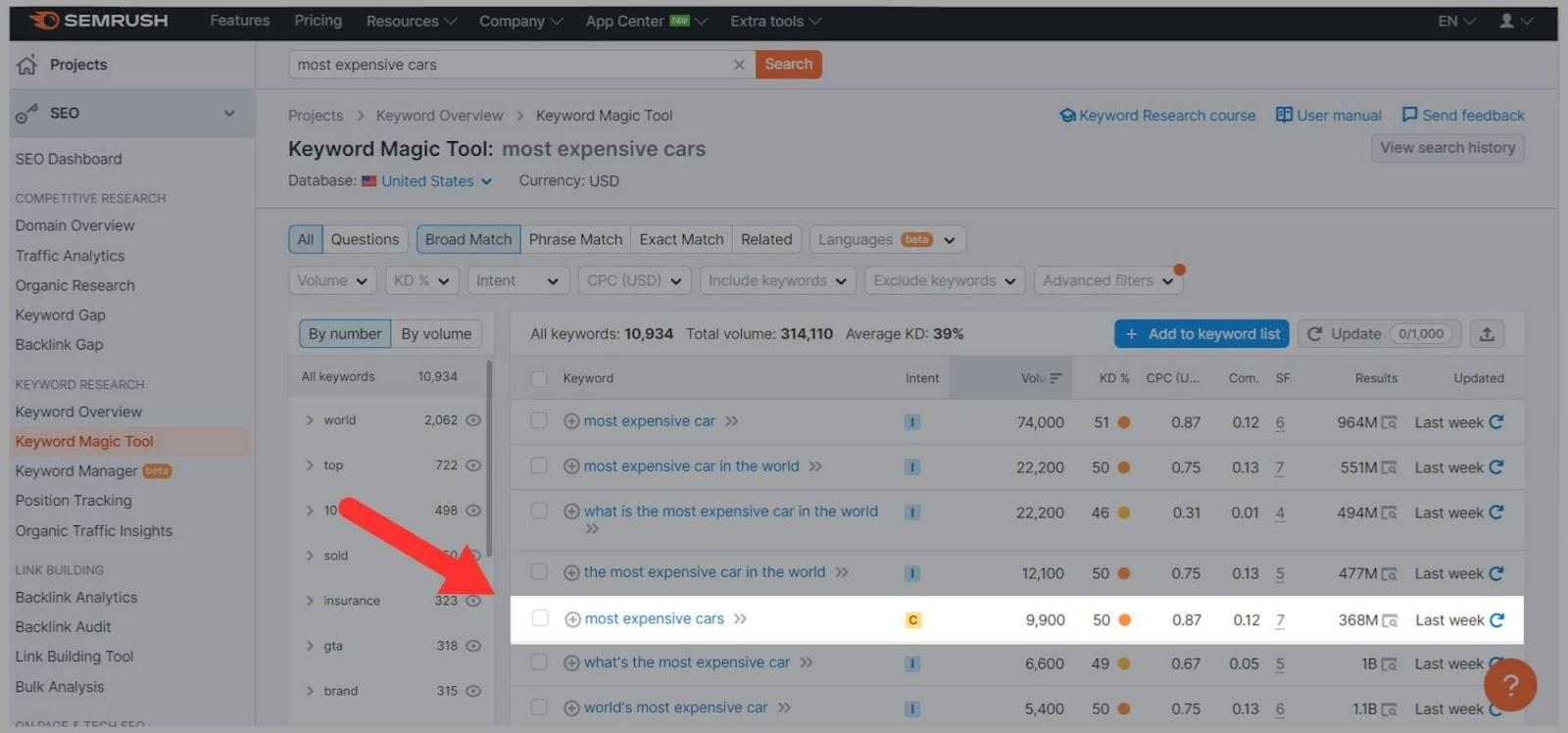
You can use Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool to assess how difficult it will be to rank for a specific keyword.
Here, I typed in the keyword ‘most expensive cars’ and the tool showed me the keyword difficulty.
Relevance
Relevance is another important factor in keyword research.
It’s nice if a keyword has a high amount of search volume. Yet, if it’s not relevant to your website, then it’s of no use to you.
If you’re a digital marketing company, then you don’t want to appear in the search results for keywords like ‘dog food’.
Relevance might seem like SEO basics 101. But it can get a little tricky at times.
Let’s look at another example.
If you have a budget vacation rentals website it might not be the best idea to target the keyword ‘luxury vacation rentals’. If your target audience is budget-conscious travelers, targeting this could mean you attract the wrong audience.
Instead, you should focus on keywords that resonate with your target audience’s preferences. This will ensure you drive the right type of traffic to your site.
Search Intent
Search intent is another crucial part of keyword research.
So what does it mean?
Search intent is the underlying motivation behind a user’s search query. For example, the search intent behind my keyword above was that I was looking for information about the most expensive cars in the world.
Let’s take a look at the different types of search intent:
- Informational intent: Users looking for answers or specific information (e.g. ‘how to lose weight’).
- Navigational intent: Users looking for a specific website or online destination (e.g. ‘Facebook login’).
- Transactional intent: Users are ready to make a purchase or engage in a transaction (e.g. ‘best DLR cameras under $1,000’).
- Local intent: Users looking for local businesses or services (e.g. ‘pizza delivery near me’).
You should always align your content and keyword strategy with search intent.
If I wanted to create content that aligns with the search intent for ‘most expensive cars’ then I could create a blog post about the most expensive cars in the US, for example.
Tailoring your content to match search intent helps to improve your rankings and create a better user experience.
It’s a win for everybody.
Short-tail and Long-tail keywords
Short-tail keywords, like ‘cleaning services’, cast a wide net. They have a high search volume but intense competition.
On the flip side, long-tail keywords, such as ’emergency cleaning services in Los Angeles’, offer a laser-focused approach. This attracts a niche audience with a lower search volume, but higher conversion potential. These keywords are also generally easier to rank for.
By targeting both short-tail and long-tail keywords, you can strike the right balance between broad visibility and targeted precision.
Using Keyword Tools
So, how do you actually go about conducting your keyword research?
You’ll need to make use of keyword tools like Google’s Keyword Planner and Semrush’s Keyword Research Toolkit.
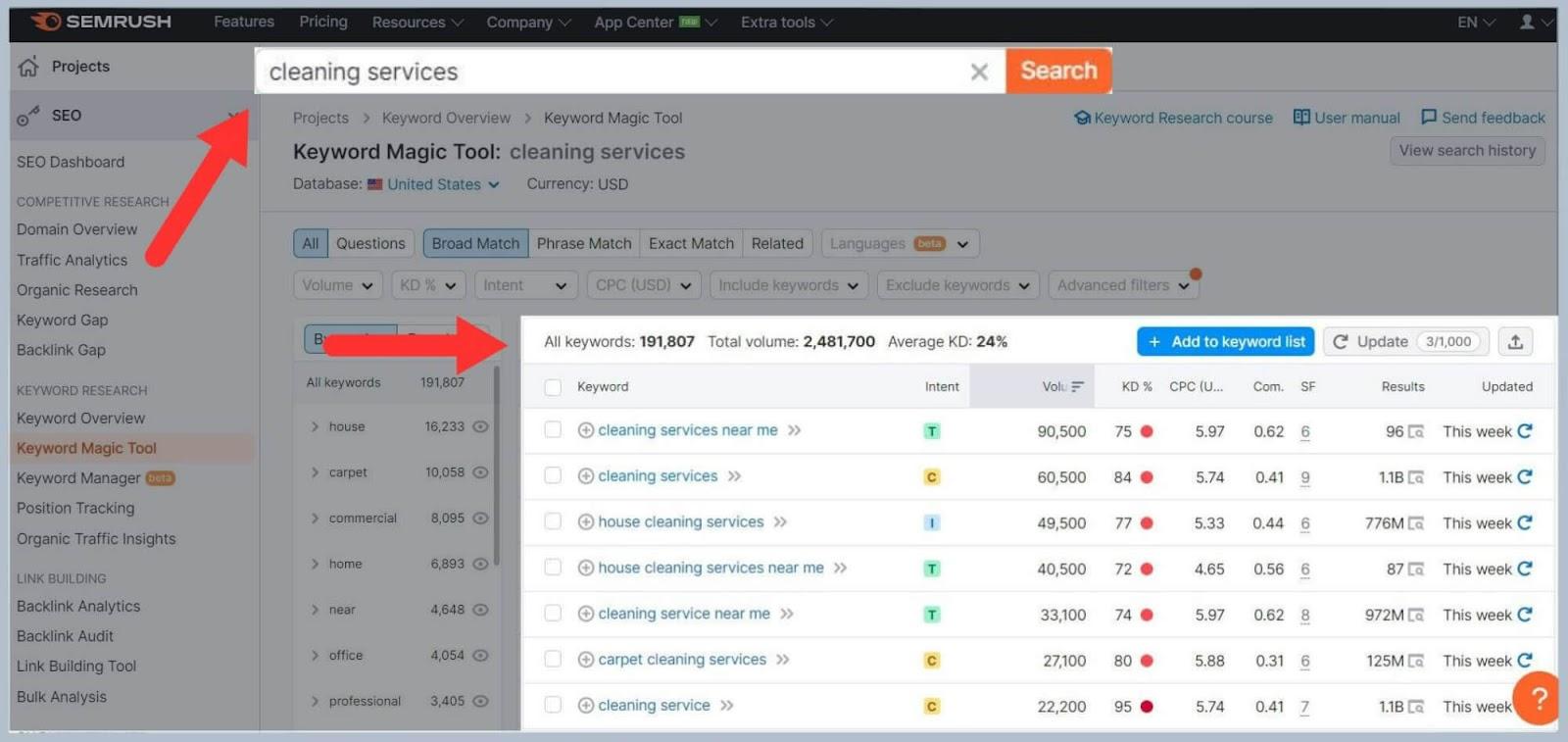
The Keyword Magic Tool from Semrush allows you to take a ‘seed’ keyword and generate thousands of keyword ideas.
Here, I typed in the keyword ‘cleaning services’ and Semrush suggested LOADS of related keywords.
You can also use their Organic Research Tool to assess what terms your competitors are ranking for.
Here, I imagined I run a site that sells musical equipment. So, one of my competitors would be guitarcenter.com.
I opened Semrush’s Organic Research Tool and typed guitarcenter.com into the search bar.
I can then see the top keywords that the competitor is ranking for.

Pretty handy, eh?
Google Search Console is another useful tool.
It provides you with a performance report for your website that shows you which keywords are generating clicks and impressions.
With this information, you can see where your SEO strategy is performing well and where there is room for improvement.
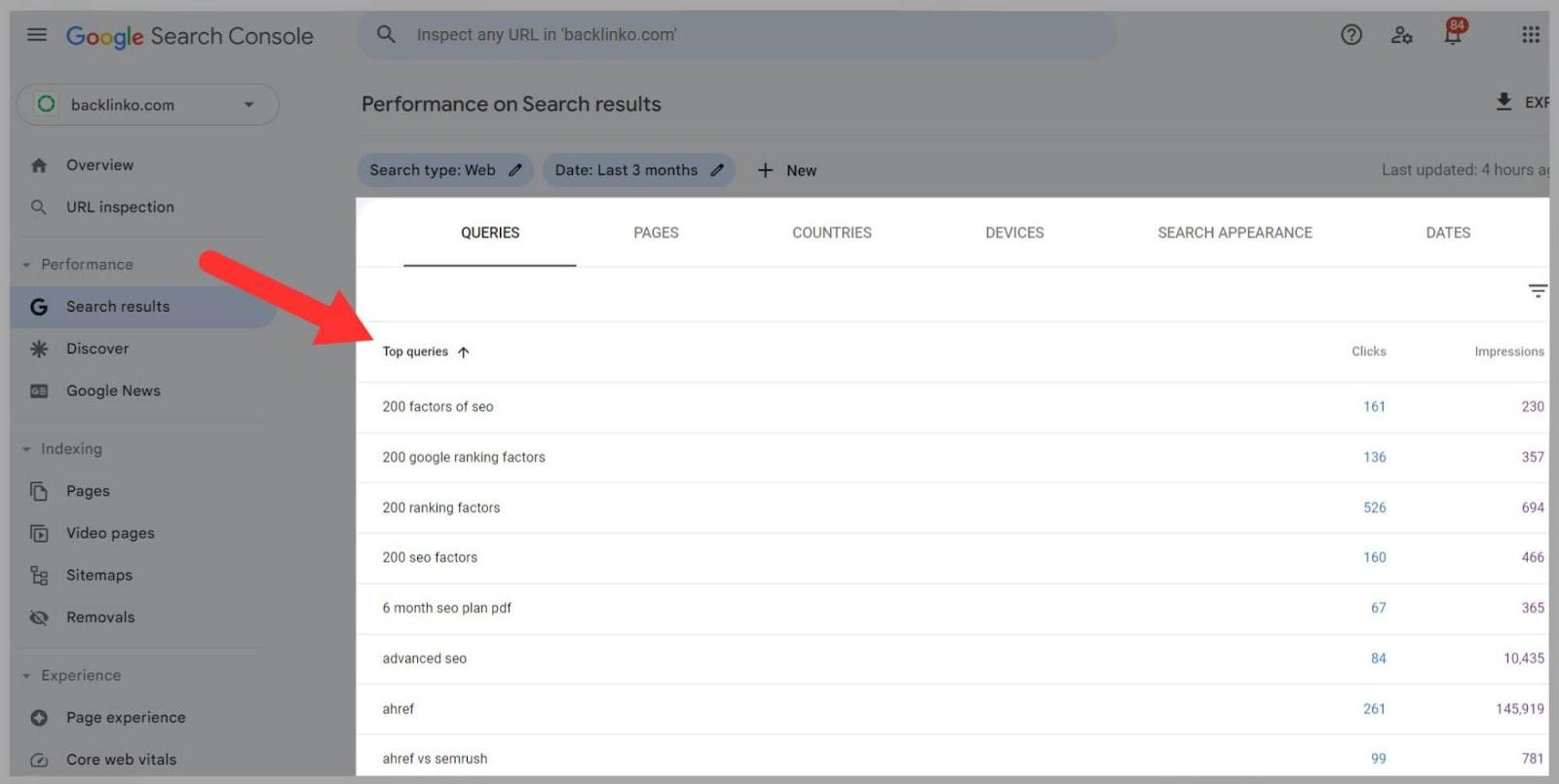
For example, here I logged into Google Search Console. The tool then gave me an overview of my site’s performance.

I then clicked on the ‘Search Results’ tab and scrolled down the page where it showed me the results for certain queries.

Next, I clicked on the ‘Top queries’ option and the tool showed me the clicks and impressions for certain keywords.
Header Tags (H Tags)
Header tags are another one of the important SEO basics.
So what are they?
They’re HTML tags that show the browser what styling should be used when displaying a piece of text on a web page.
For example, the HTML for the heading in this section would look similar to this:
<h3>Header Tags (H Tags)<h3>
Header tags follow a hierarchy and they title the content below them or introduce it.
The hierarchy for header tags is:
- H1 tags: indicate the most important text in a piece of content. This is usually the title or the main theme of the piece.
- H2 and H3 tags: are both used as subheadings. H3s are lower in the hierarchy than H2s (as you might have guessed). So, they’re only used after H2s.
- H4, H5, and H6 tags: are used to give additional structure within the subsections.
The reason header tags are important is that they help Google and other search engines understand the content you create. They create a hierarchy of information on the page and provide some context.
They also make your content more accessible and readable, which means it’s much more user-friendly. In other words, you can use them to break up large walls of text. Additionally, they make your article easier to skim through.
Imagine trying to read a novel that didn’t have any chapters. Well, imagine trying to read a blog post with no headings. Doesn’t sound too appealing, does it?
Google pays close attention to your header tags.
That means you should include keywords within them.
Now, the main aim of your content is to provide value to the reader and to be very readable. With this in mind, you want to avoid stuffing your headings with keywords.
Still, if your main keyword is ‘best restaurants in Barcelona’, then you need to ensure that at least some of your headings contain keywords related to this or variations of your primary keyword.
You should always include your main keyword in the H1 tag.
Body Content
To maximize its impact, it’s essential that you create unique, high-quality content. Within your body content, you also need to strategically incorporate the keywords you’re targeting.
Remember I mentioned search intent earlier?
Well, the content you create must match the search intent of your target audience. You should also use internal links embedded within your content to guide users to other relevant pages.
Body content is the text that appears after your H1 tag. It’s vital for driving organic traffic, enhancing user engagement, and boosting your content’s shareability.
This is where the main content of your article will appear. The more value it adds to the user, the better the chances of readers staying on your site, which enhances user engagement.
Let’s take a look at the best ways to optimize your body content.
High-quality content with a Fresh perspective
There is a LOT of content online. This means that uniqueness is key. You should aim to craft compelling content that offers valuable insights, actionable advice, and fresh perspectives.
Try to think of yourself as a thought leader within your industry.
What are the topics that other sites haven’t covered extensively?
Or can you do a better job of covering the topics they’ve already covered?
Consider what you can do to provide more value to the user. This could include additional content like videos and images.
Address these topics and engage your readers with captivating storytelling and well-researched content that keeps them coming back for more.
Strategic placement of keywords
Utilize the keywords you’ve identified to determine what content you should create. Then, use them strategically throughout your body content for maximum SEO impact.
You should signal topic relevance to search engines by including the main keyword in your introduction.
Also, be sure to sprinkle keywords naturally throughout the body content to maintain a contextual flow.
Contextually relevant usage
Keyword usage should feel organic and seamless. Don’t force keywords in where they don’t fit naturally (this is called keyword stuffing). Instead, prioritize context and readability.
I like to think of it as salting a dish. A nice dusting of salt is just right and adds to the experience. Yet, a huge handful of salt thrown in for the sake of it completely ruins it.
The same is true of using keywords in your body content.
Use synonyms, variations, and terms related to the main keyword. This creates a comprehensive picture of the topic and enhances the overall user experience.
As with too much salt in a dish, stuffing your content with keywords negatively affects the reader’s experience. Keyword stuffing doesn’t just harm your SEO efforts but is also considered to be a black hat technique. Google really doesn’t like keyword stuffing and your site may get penalized if you do it.
Here’s an example of keyword stuffing.

Pretty horrible to read, right?
So, make sure that you maintain a healthy keyword density. This way, your content will remain informative, engaging, and search-engine friendly.
Meta Title
Meta titles, or title tags, are HTML elements that define the title of a web page.
They’re concise summaries of a web page’s content. They give search engines and users an idea of what to expect when they click through to your webpage.
Here’s an example:

As you can see, meta titles are displayed prominently in the SERP. This means they’re the first impression users have of your page.
Meta titles should be clear, descriptive, and accurately reflect the content of your web page. You should also include relevant keywords that align with the search intent of the user.
You should also keep them nice and concise. Keep them to around 50 to 60 characters to avoid them being cut off when they’re displayed in the SERP.
Meta Descriptions
Meta descriptions are concise snippets of text that summarize web page content. They don’t directly impact rankings in search results pages, but they’re important for enticing users to click on your pages.

Here’s why meta descriptions matter:
- Boosts Click-Through Rates (CTR): A well-crafted meta description increases CTR by attracting users with an appealing and relevant preview. CTR measures the percentage of users who actually click on your page when it appears.
- Enhances user engagement: Accurate meta descriptions set expectations for your content. They encourage users to engage with it and convince them that your content will answer the query they have.
To create effective meta descriptions, you should craft snippets that accurately represent your content. They should include persuasive language, relevant keywords, and clear a call to action (CTA).
It’s best to keep them as concise as possible. Generally, a meta description should be around 156-160 characters.
URL Structure
Next up in our breakdown of on-page SEO basics is the excitingly named URL structure.
It may sound a bit dull but a well-structured URL is crucial for both search engines and users.
The way that these URLs are organized and structured impacts user experience and your rankings in the search results pages.
Here’s how to make sure your URL structure is optimized for maximum effectiveness:
- Logical organization: Craft URLs that reflect the hierarchy and organization of your website’s content. A logical structure helps search engines understand the relationship between pages and improves user navigation.
- Keyword integration: Incorporate relevant keywords into your URLs to enhance their visibility and indicate content relevance. This can positively impact search engine rankings and improve the likelihood of attracting organic traffic.
- Avoid random dates and symbols: Steer clear of unnecessary symbols, dates, or random characters in your URLs. Clear, concise URLs are more user-friendly, easier to remember, and shareable.
- Hyphens for word separation: Use hyphens to separate words within your URLs instead of underscores or spaces. Hyphens are preferred by search engines and make URLs more readable for users.
See, it’s not quite as boring as it sounds.
Images
Optimizing images is another one of the important SEO basics. There are two key elements you need to focus on when optimizing images. These are descriptive file names and alternative text (alt text).
Alt text is a textual description that’s added to HTML image tags. If an image can’t be displayed, the alt text is shown instead. It provides context and describes the purpose and content of an image.
But how do you optimize descriptive file names and alt text? Let me show you.
- Descriptive file names: You should rename image files with descriptive keywords instead of generic names. For example, for this article, I could use ‘seo-basics.jpg’ instead of ‘image123.jpg’. This provides valuable context to search engines and helps them understand the image’s relevance to the content.
- Alt text: Adding descriptive alt text to your images assists visually impaired users and provides additional information to search engines. Be sure to use concise and relevant descriptions, and incorporate keywords when appropriate.
For example, a piece of alt text might read ‘Woman wearing blue running shoes jogging on a scenic trail in the forest during sunset’.
Internal Links
Internal links are another important part of on-page search engine optimization. An internal link is a hyperlink from one page of your site to another.
But before we get into them, I need to tell you about a term called link equity.
Link equity, or link juice, refers to the value or authority passed from one web page to another through hyperlinks.
When a web page receives an external link from another reputable or high-authority site, some of that authority is transferred to the linked page.
This improves its credibility and potentially its search rankings too.
Internal links within your own website also contribute to link equity distribution. By strategically interconnecting relevant pages on your site, internal linking helps you to pass link equity and signal relevance to search engines.
OK, so internal linking is good for distributing link equity. Pretty neat, but is that it?
It sure isn’t. Here are some other ways it helps both search engines and users. Plus, some tips on how to use internal linking effectively:
Link Equity and Site Architecture
By distributing link equity throughout your site, internal links impact how search engines understand and rank your pages.
Imagine your website as a house filled with different rooms. Just as pillars support that structure, strategic internal links within your site act as pillars that pass on link equity.
These links signal to search engines the relevance and importance of those pages. This strengthens the overall structure of your website.
SEO and user experience benefits
Internal linking also improves the crawlability of your website. It allows search engines to discover and index more of your content.
Using internal links provides clear navigation and facilitates content discovery. This enhances user experience by encouraging visitors to explore related topics and spend more time on your site.
Use logical and relevant internal links
Create a logical linking structure by interlinking relevant pages within your website. For example, if you have a page titled ‘Birds of Prey’ you could link it to other pages that cover related topics like ‘What’s the Rarest Bird of Prey?’.
This helps you to prioritize user intent and context to guide visitors to valuable resources.
Anchor Text Optimization
Anchor text is the clickable text of a link. You can optimize this text by using keyword-rich phrases that accurately represent the linked page’s content. This helps search engines understand the linked page’s relevance and improves keyword association.
Here’s an example from my own site:

Clicking on ‘squeeze page’ takes you to one of my other blogs called ‘How To Create a Squeeze Page’.
Off-Page SEO
As the name suggests, off-page SEO is focused on the external factors that can improve your site’s rankings.
It involves activities like link building, social media marketing, and online mentions. The aim is to influence how others perceive and interact with your site.
Link Building
Link building involves gaining links, called backlinks, from reputable websites to your own web pages. High-quality backlinks act as votes of confidence. They signal to a search engine the value and relevance of your content.
Let’s examine the ways you can go about getting yourself some top-notch backlinks:
- Natural links: This is when others naturally discover your content and link to it. These organic backlinks are highly valued. Creating compelling and shareable content increases the likelihood of earning natural links, which boosts your website’s credibility, authority, and rankings.
- Manually built links: This involves earning links by establishing connections with other site owners through outreach. One of the best ways to do this is by creating guest posts for other sites. This involves crafting engaging content that can be posted on sites with links back to your site.
Another way of earning manually built links is reaching out to influencers and industry experts to arrange collaborations.
One of the best tools for creating an outreach campaign to earn backlinks is Semrush’s Link Building Tool.
It helps you to build a list of outreach prospects based on your competitors and target keywords. This makes it easier to acquire links and monitor the progress of your campaigns.
Quality trumps quantity when it comes to backlinks. Focus on acquiring links from authoritative and relevant sources. Search engines prioritize the quality of backlinks over sheer quantity.
By mastering the art of link building, you can gradually build the authority of your site and improve its search engine rankings. This is without a doubt one of the most important SEO basics.
Social Media Marketing
Did you know that 37% of adults in the US use Instagram?
How about the fact it only takes 0.25% of a second of exposure for a Facebook user to be able to recall a piece of content?
What does this tell you?
It should tell you that social media marketing is an important part of SEO.
But how can you use it?
- Boosting your content: Expand your content’s reach and engagement by posting it on your social media platforms. This will help to drive significant traffic to your site.
- Trust building: Establish credibility by actively engaging with your audience, addressing concerns, and delivering value.
Influencer Marketing
Influencer marketing allows you to tap into an existing audience that aligns with your target market. Overall, it should help you achieve higher search engine rankings, gain backlinks, and experience a boost in sales.
Collaborating with influencers exposes your brand to their dedicated and engaged audience. This could expand your reach and drive targeted traffic to your site.
For example, let’s say you run a small online fashion store.
If you partner with a popular fashion influencer they can showcase your latest collection to their large following.
Their followers trust and value the influencer’s recommendations. This means they’re likely to visit your website, and potentially make purchases.
As a result, your brand awareness is increased and your customer base is expanded.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO is vital as it ensures search engine bots can crawl, understand, index, and rank your website.
It also focuses on things like optimizing site speed to improve user experience, increasing site security with SSL certificates, and creating XML sitemaps.
Technical SEO helps you to address issues with your site and to make sure you’re using the current best practices.
Check for Crawling and Indexing Issues with Google Search Console
Google Search Console is great for helping you to gain insights into how Google sees and analyzes your web pages.
When you connect your site to the tool, it alerts you to any crawling and indexing issues it has.
It can show you which pages haven’t been indexed by Google and why they haven’t been.
I opened Google Search Console and clicked on the ‘Pages’ tab to see crawling and indexing issues for my own site. The first page shows me how many pages have been indexed and how many haven’t.

To find out why, all I had to do was scroll down.
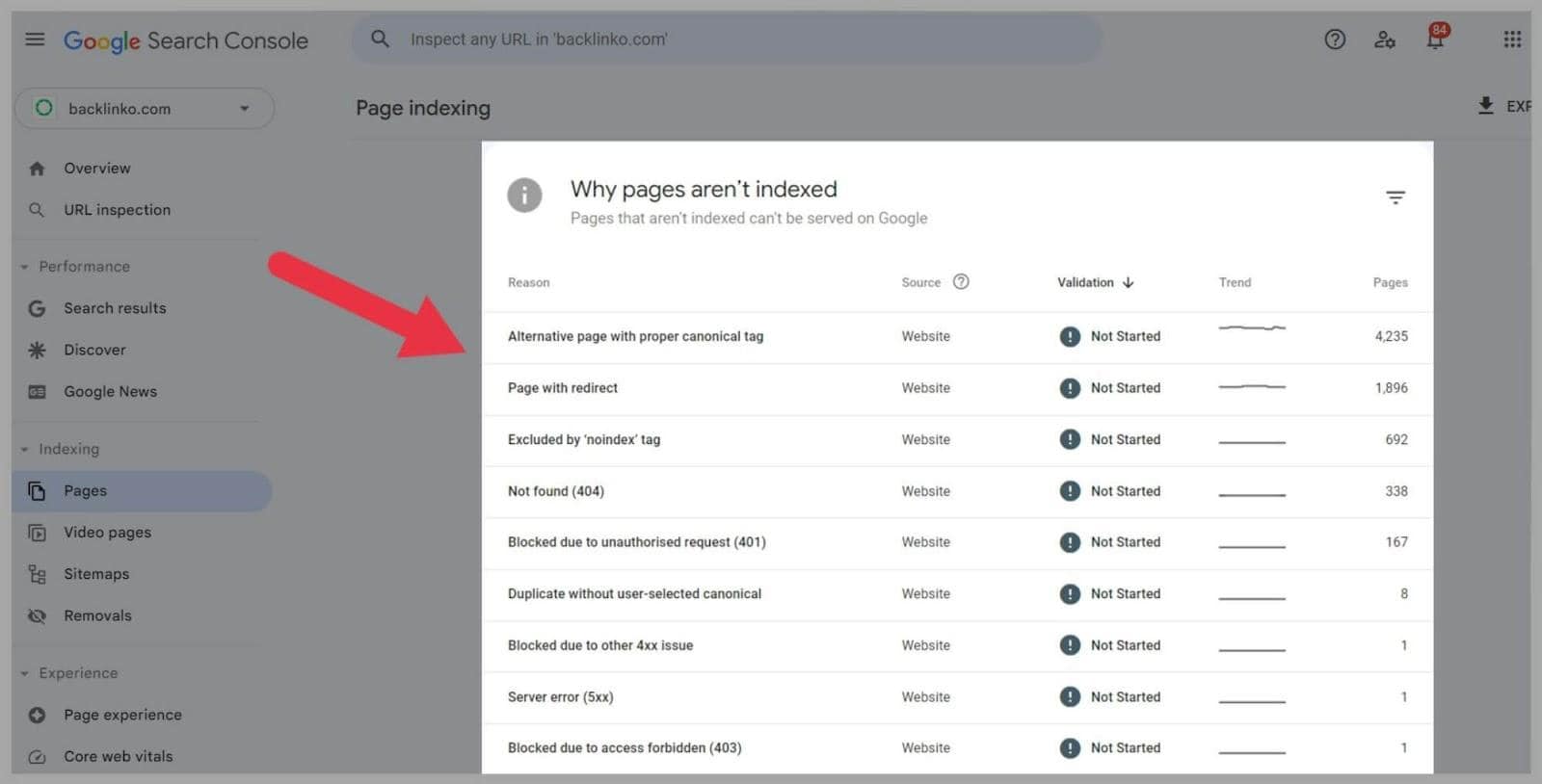
If Google finds it tough to crawl your site then some pages, or even your whole website, might not be indexed.
Mobile Friendliness
In the first three months of 2023, 58.33% of global website traffic came from mobile devices.
Clearly, responsive mobile-friendly websites have never been more important.
Google values user experience very highly when rankings sites.
And, since so much traffic comes from mobile devices, the user experience on your site will definitely be hurt if it’s not mobile-friendly.
Picture this:
You’re on your mobile phone browsing for local Chinese restaurants.
You click on a search result and land on a page that’s not optimized for mobile devices.
You spend the next few minutes awkwardly zooming in to try and read the menu.
Does that sound like a good user experience?
Didn’t think so.
Well, Google agrees. It now uses what’s called mobile-first indexing. This means its algorithms no longer use the desktop version of a website when crawling and indexing. Instead, they focus solely on the mobile version.
To avoid your rankings suffering, you need to make sure your website is mobile-friendly.
Here are some things you can do:
- Optimize page loading speeds for mobile devices (I’ll cover loading speeds in more detail later).
- Ensure links and buttons are easily tappable.
- Make sure the text is easy to read without zooming in.
- Use a responsive design that adapts to different screen sizes.
Core Web Vitals
I already mentioned how much Google focuses on user experience when it comes to rankings.
Well, a big part of user experience is how quickly it takes elements of a page to load.
Enter Core Web Vitals.
They’re a set of essential metrics that evaluate key aspects of user experience.
If you optimize for Core Web Vitals, your site will have faster loading times, improved interactivity, and a visually stable experience.
- Faster loading times: Optimizing for core web vitals ensures that your site loads quickly. This keeps visitors engaged and reduces bounce rates.
- Improved interactivity: By optimizing for metrics such as First Input Delay (FID), you reduce the delay between user interactions (clicks, taps, etc.) and the site’s response. This creates a smooth and responsive browsing experience.
- Visual stability: If you optimize for Core Web Vitals, it prevents the layouts of your pages from shifting around unexpectedly. This makes them less frustrating to use and improves user engagement.
This won’t just enhance user satisfaction but will also boost your search engine rankings.
That’s a win-win in my books.
XML Sitemap
An XML sitemap is a file that lists the pages on your website. This helps search engines understand its structure and index content more effectively.
They lay out a blueprint to guide crawlers through your site so that your valuable pages are crawled, indexed, and displayed in search results.
XML sitemaps include important information about each page on your website such as its priority, modification date, and update frequency.
If you want to see the XML sitemap for your site, it’s really easy.
All you need to do is type in /sitemap.xml at the end of your domain.
I typed backlinko.com/sitemap.xml into Google and this is what I saw.

Search engines LOVE this type of information. It makes discovering and indexing your content straightforward for them.
I think it’s fair to say that the web is a pretty big place.
That’s why search engines must easily understand your website and effortlessly find your valuable content.
XML sitemaps make it easy for search engines to navigate your site with precision and efficiency.
There are several ways to go about creating a sitemap. If you use a content management system (CMS) like WordPress, Squarespace, or Wix then they’ll create it automatically for you.
If you want to have control over your sitemap (rather than leaving a CMS in full control) then you can use a WordPress plugin like Yoast SEO.
You could also create your sitemap manually but this is VERY time-consuming. It’s usually best to use a sitemap generator such as Sitemap Writer Pro.
If you want to learn how to set up a fully optimized sitemap, then check out my blog on how to do this.
Site Security
Site security is everything you put in place to protect your site and your users. It helps you to keep user data safe and to prevent cyber-attacks against your site.
In 2022, 19.7% of global retail sales took place online.
Naturally, this means that web users are more concerned with site security than ever before.
And it’s not just users.
Google and other search engines also prioritize user safety and place a high value on-site security.
So, how do you optimize your site’s security to make sure it ranks highly in the search results pages?
That’s where SSL certificates come in.
SSL certificates encrypt the data that’s exchanged between your site and visitors. This thwarts potential cyber-attacks and instills confidence in users.
When your site is protected by an SSL certificate, visitors will see a padlock displayed in the address bar.

Plus, having an SSL certificate means that the acronym HTTPS appears in your site’s URL. This stands for Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure. Without an SSL certificate, the URL will display HTTP instead.
This stands for the same thing but without that crucial word, secure.
Investing in site security doesn’t just safeguard your website and its users. It also propels your SEO endeavors.
It fosters trust, enhances user experience, and aligns with search engine guidelines. This paves the way for higher rankings—provided all other aspects of your SEO strategy work together.
Schema Markup
Schema markup is a standardized code language that adds additional information to website content. It helps search engines understand and interpret it more effectively.
It uses structured data to provide context and categorize elements on a webpage such as product details, reviews, event information, and much more.
Here’s why it’s important for SEO:
- Improves relevance: When you categorize and label your content with schema markup, you provide search engines with precise context. This makes your website more relevant to users’ search queries.
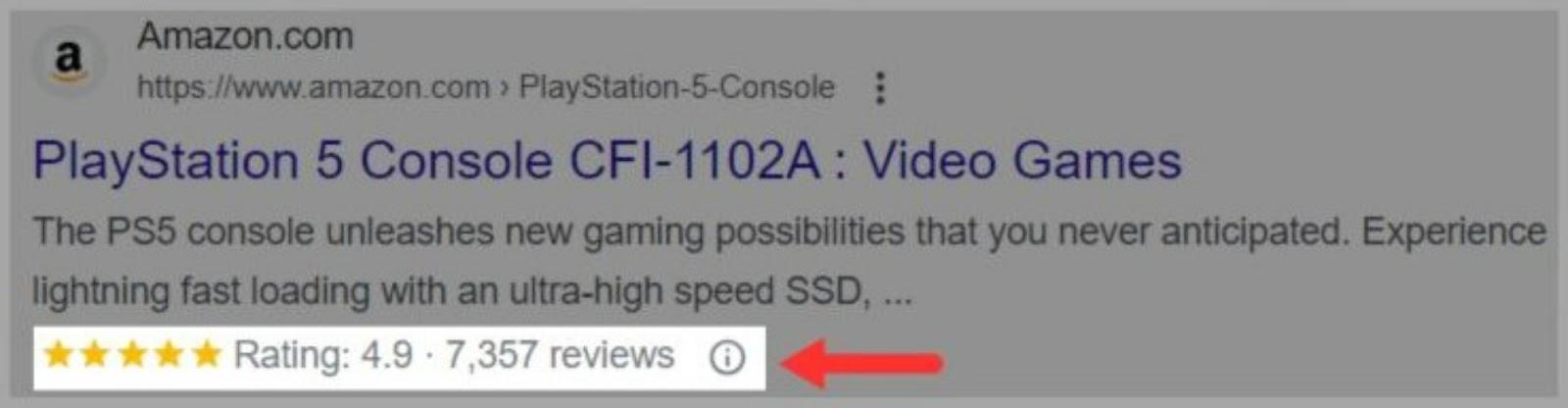
- Richer search results: It allows you to showcase additional information such as ratings, reviews, and prices directly in search results. This gives users a sneak peek into your content which attracts attention and increases click-through rates.
Here’s an example of schema markup in action:
Optimize Images
Earlier, I talked about the importance of images in terms of on-page SEO. They’re also a crucial part of technical SEO.
By optimizing images, you can improve the loading speeds of your web pages. This improves user experience and can contribute towards higher rankings in the SERP.
One of the keys to optimizing your site’s images is compressing them without sacrificing quality. You can do this by choosing the right file format.
For example, if you want to compress a complex image like a photograph then the JPEG file format is most commonly used.
This format reduces the file size by discarding some image data that are less perceptible to the human eye. This allows for significant size reduction while maintaining decent image quality.
Optimizing image dimensions is also important.
By resizing images to fit their intended display size, the file size is reduced and faster loading occurs on different devices.
This allows images to adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and optimizes the browsing experience for mobile users.
Overall, image optimization creates a faster and more engaging user experience.
Local SEO
Local SEO is the process of optimizing a website to improve its visibility within location-based searches.
It helps businesses to make sure they appear prominently in search results when users search for products or services within a specific location.
Two of the key components of local SEO are Google Business Profile and Google’s map pack:
- Google Business Profile: This provides a comprehensive overview of your business’s details such as contact information, opening hours, location, and customer reviews.

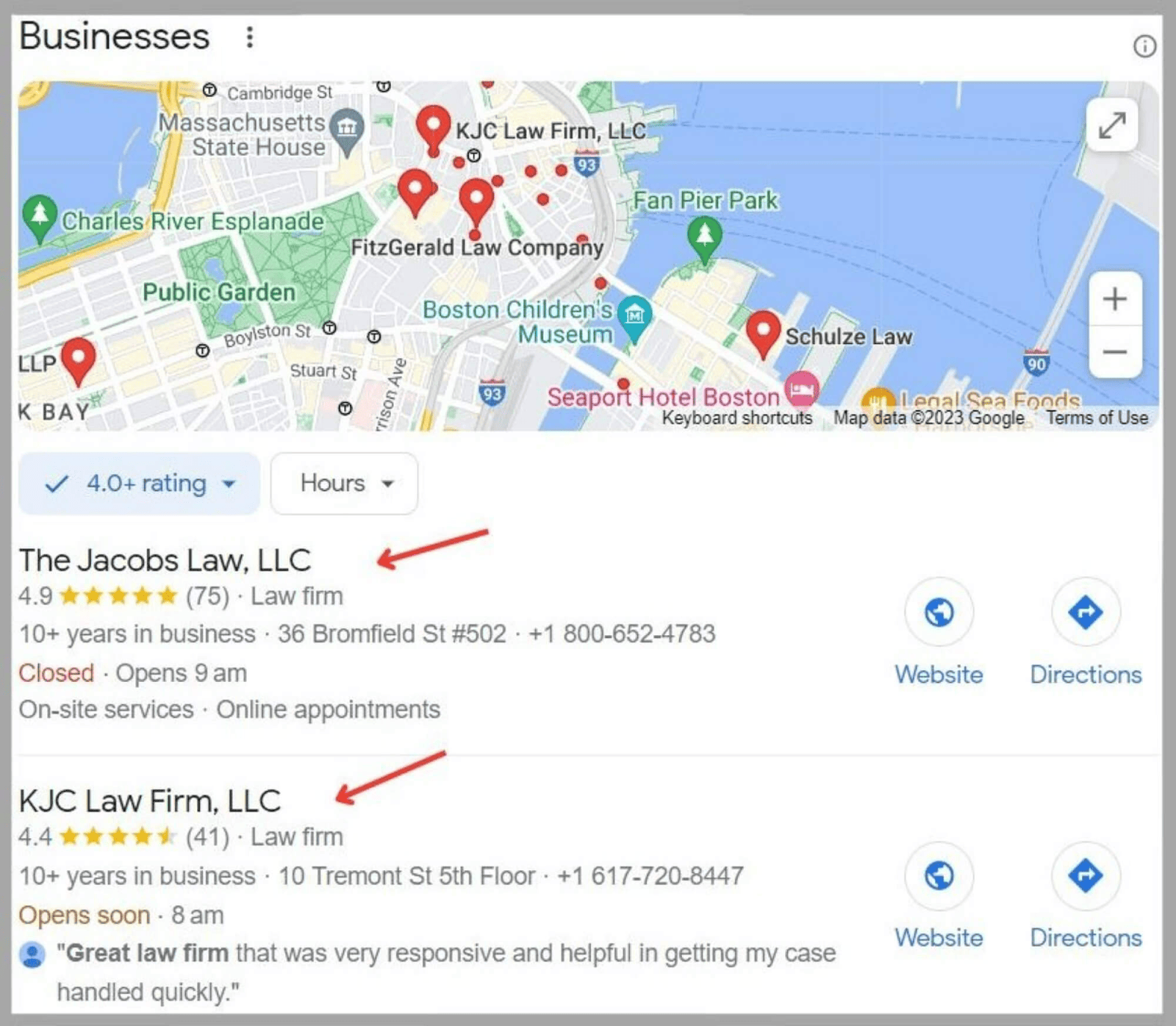
- Map pack: The map pack showcases a set of local businesses on a map near the top of the search results. This gives users quick access to the websites of local businesses. For instance, a search for ‘best law firms in Boston’ brings up this:
To excel in local SEO, our old friend keyword research is important. You need to identify and target keywords with local intent.
Let’s look at an example of this.
Imagine you own a bakery in San Francisco.
You start off by identifying general bakery-related keywords like ‘bakery’, ‘pastry shop’, and ‘freshly baked goods’.
Then, you add in location-specific modifiers like ‘San Francisco’, ‘SF’, or even specific areas like ‘Mission District’.
You should also consider user intent. These are the specific needs or queries a potential customer might have when searching for bakeries in your area.
This could be ‘best croissants in San Francisco’ for instance.
You can use a tool like Semrush’s Keyword Magic Tool to see the search volumes and competition for the local intent keywords you’ve identified.
The Keyword Magic Tool also suggests plenty of other keyword options that you could use for local SEO.
When I typed in the keywords I just mentioned this is what it gave me:
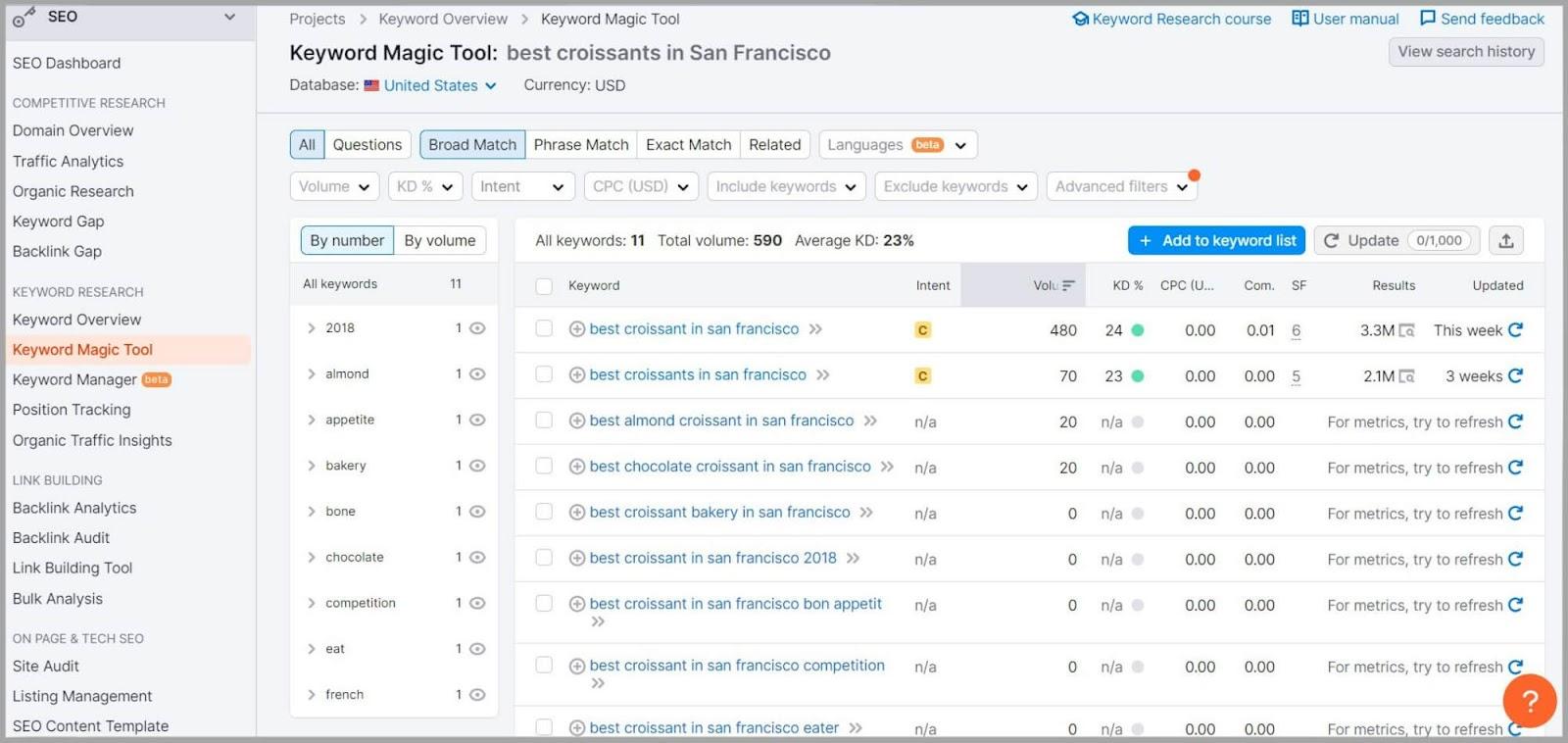
By targeting keywords like this, you can align your website with the specific needs and queries of your local audience.
This increases your chances of attracting relevant traffic and driving more customers to your business.
Tracking Your SEO Results
As you can see, search engine optimization is crucial for all types of websites.
But how do you measure the success of your own SEO strategy?
Well, this depends on the type of business you run and the goals you want to achieve.
Still, there are some fundamental metrics that every business should keep track of.
Organic Traffic
The first metric to pay attention to is organic traffic.
You can track this by using Google Analytics.
Here’s how to do it:
In Google Analytics, go to the ‘Acquisition’ tab on the left-hand sidebar.

Choose ‘All Traffic’ and then ‘Channels’.
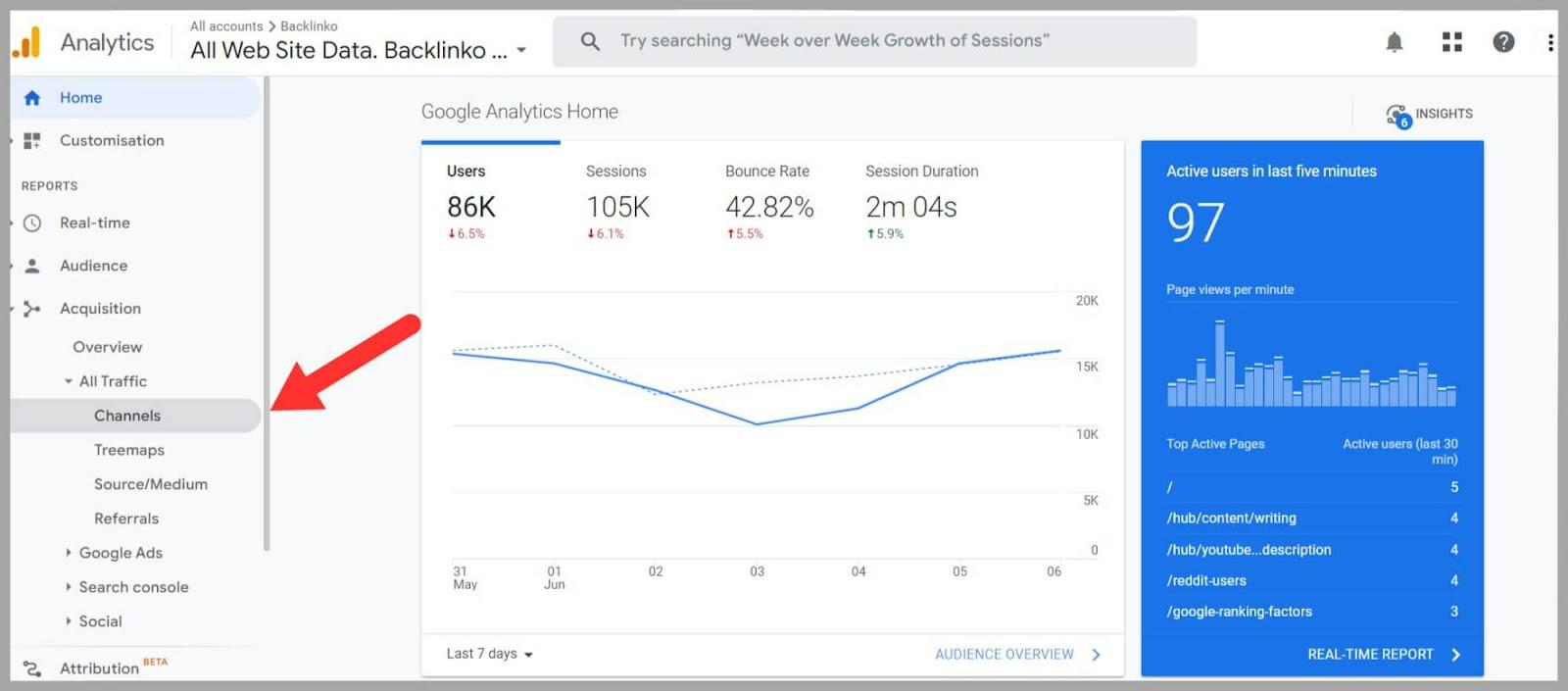
Find the ‘Organic Search’ channel. This represents the traffic generated by search engines. In the ‘Organic Search’ report there is lots of information. Pay close attention to metrics like users, sessions, average session duration, and bounce rate.

You can tailor the report by applying filters, adding segments, and selecting specific date ranges. This allows you to get a deeper understanding of your organic traffic patterns.
For example, if you click on the ‘Secondary Dimension’ tab it allows you to see your organic search results for different dates by clicking on the ‘Date’ option.
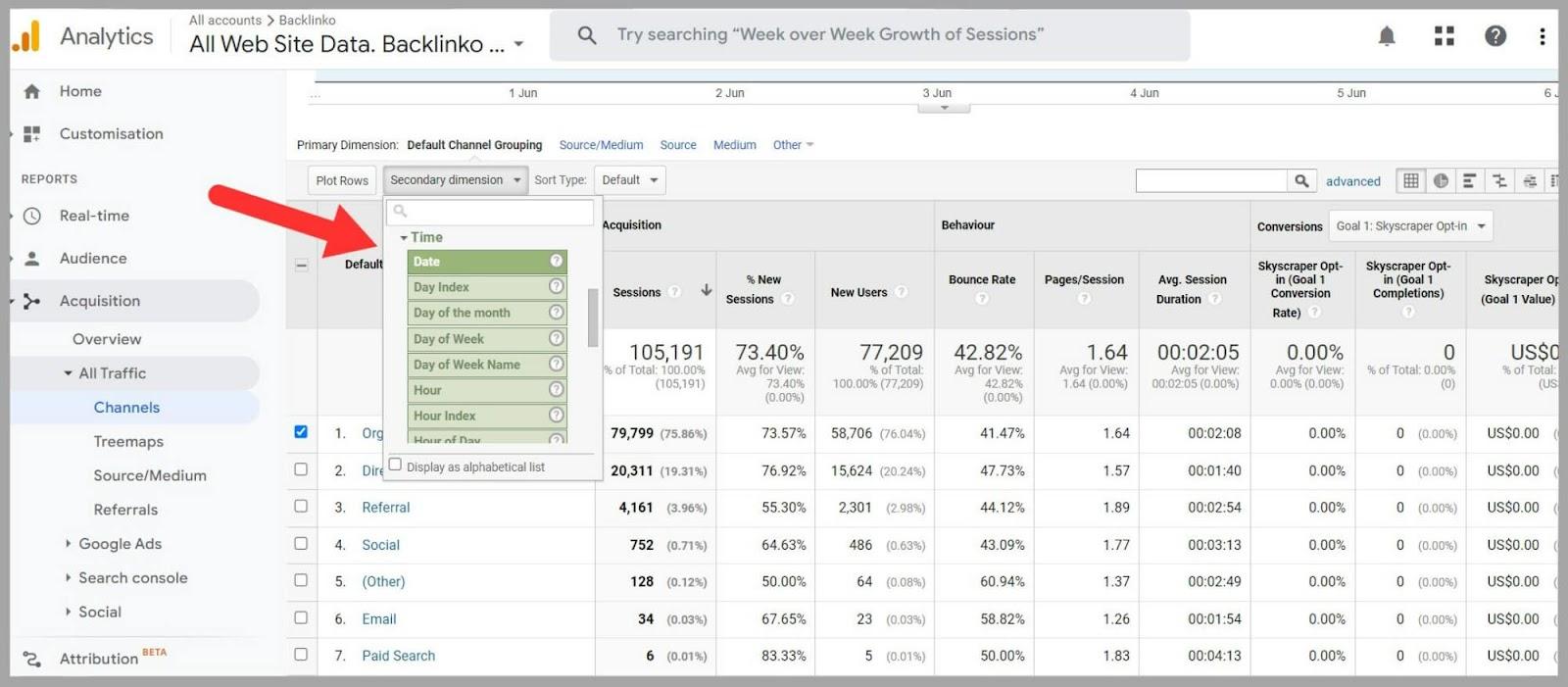
By doing the above, you can compare organic traffic data month-over-month. This means you’ll be able to spot trends and seasonal fluctuations. You can then evaluate the impact of your SEO efforts and identify areas for improvement.
Keyword Rankings
Another key metric you need to pay attention to is your site’s keyword rankings.
Keyword rankings refer to the position your web pages are achieving for specific keywords.
This shows you how well-optimized your pages are for the keywords you’re targeting.
You can use Semrush’s Position Tracking tool to effectively track your keywords.
Here’s how:
Type your domain into the search bar and click ‘Set Up Tracking’’.

Next, select which search engine you want to use to track the rankings and which device. Choose a location and language too.
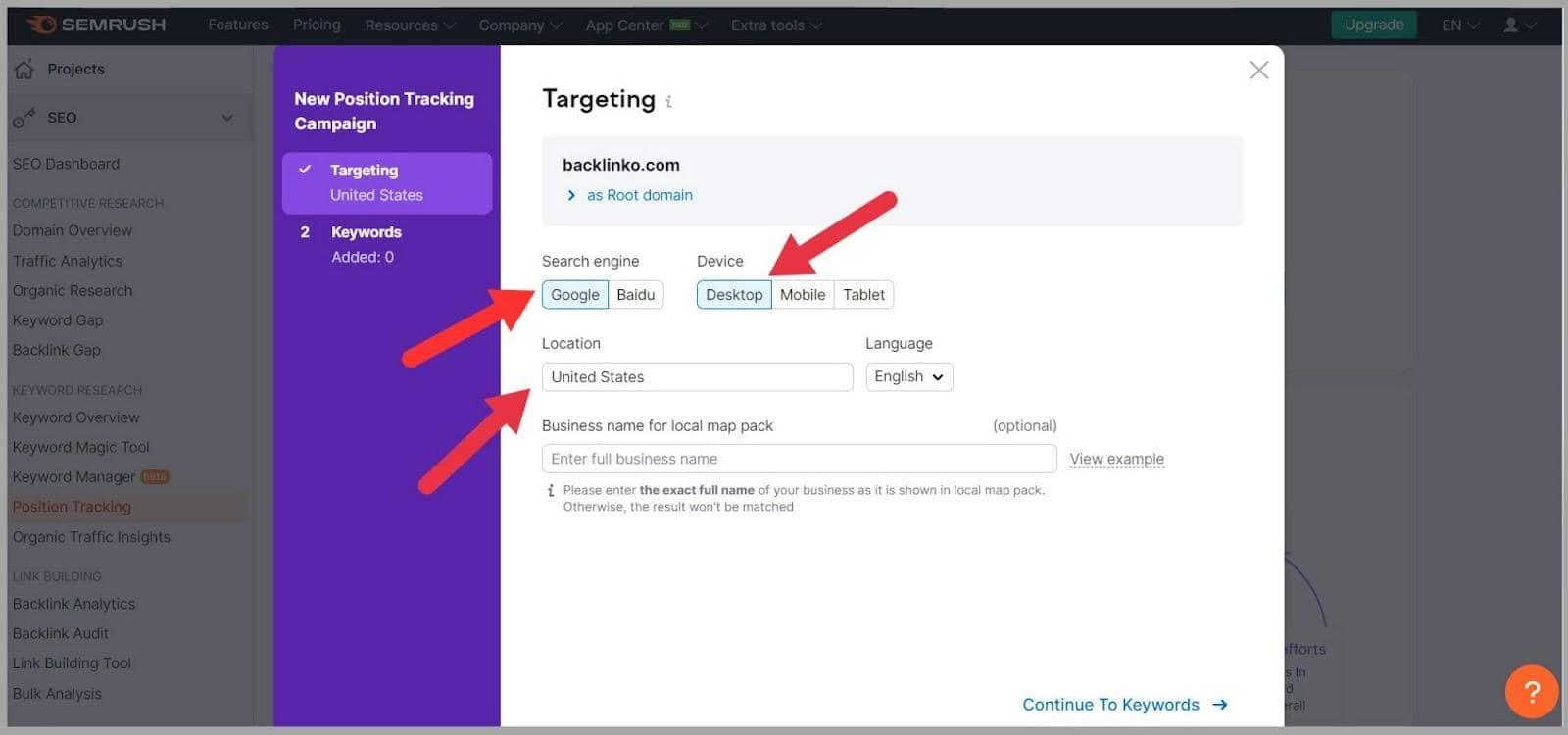
Click ‘Continue to Keywords’.
Now, type in the keywords you want to track and click ‘Start Tracking’.
You’ll now be able to view your keyword rankings in the Overview tab.
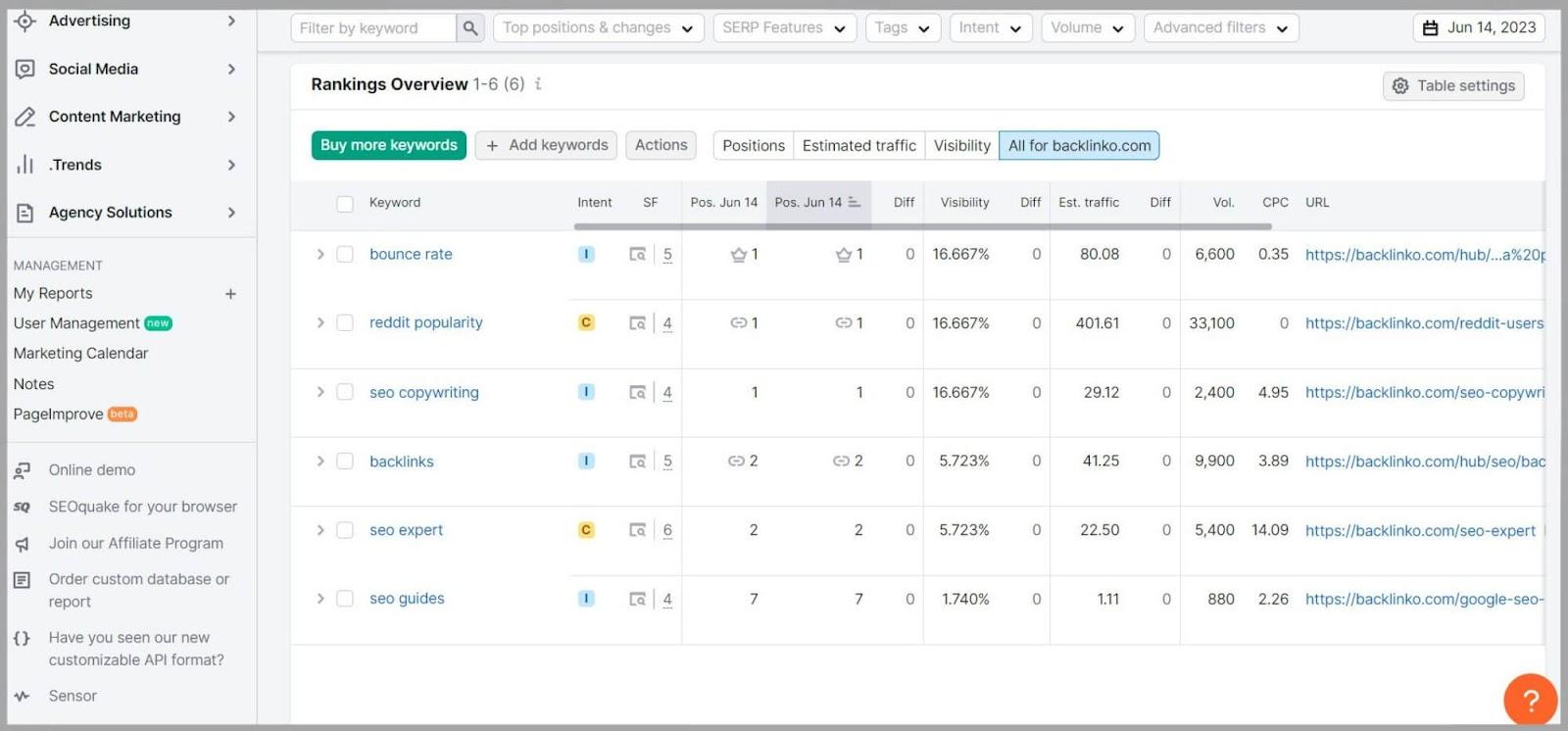
Tracking your keyword rankings is essential as it directly impacts your website’s visibility and organic traffic.
So be sure to keep on trackin’!
Organic Leads and Sales
Let’s face it, the main reason people have businesses is to make money.
This means that the primary measure of success for your website is leads, sales, revenue, and profit.
Website traffic is all well and good. But, the conversion of that traffic into tangible results is what truly defines triumph.
By monitoring organic leads and sales you gain invaluable insights into your business’s bottom-line impact.
Google Analytics is the best tool to use for tracking this.
It gives you comprehensive data on traffic, conversions, and revenue.
You can also use it to set up goals, track e-commerce transactions, and generate reports to analyze your organic leads and sales performance.
FAQs
Are there any downsides or risks to using SEO?
SEO has many benefits but there are some downsides and risks:
- Search engine algorithms constantly evolve. This makes it challenging to keep up with changing ranking factors.
- SEO results take time to materialize. They require patience and consistent effort.
- Over-optimization can lead to penalties and a loss of organic visibility.
- If you rely solely on SEO it can limit your marketing channels. You need to diversify your strategies for long-term success.
What is black hat SEO?
The term black hat SEO refers to unethical practices used to manipulate search engine rankings. The tactics involved violate search engine guidelines.
These tactics include keyword stuffing, hidden text, and spammy backlinks. Black hat SEO tactics can lead to short-term improvements in search results rankings. However, they risk penalties and long-term damage to a website’s organic visibility and reputation.
Is SEO only for large businesses?
NOPE.
SEO is a powerful strategy accessible to businesses of all sizes. Whether you’re a startup or a huge corporation, SEO can drive organic traffic and dramatically increase your rankings.
Are there specific SEO strategies for e-commerce websites?
There sure are. Specific SEO strategies for e-commerce businesses could include optimizing product pages with compelling descriptions, conducting keyword research for product categories, and encouraging user-generated content.